Blood Marker Reveals Type 2 Diabetes Risk Years In Advance
A new Swedish-led study has identified a blood marker that may show who is at risk of developing type 2 diabetes many years before the disease is typically diagnosed.

A new Swedish-led study has identified a blood marker that may show who is at risk of developing type 2 diabetes many years before the disease is typically diagnosed.

A consortium of scientists who are taking a novel approach in their research to detect the genetic variations that predispose individuals to type 2 diabetes provided an update of their findings.

Drinking black tea may help protect against type 2 diabetes, but more study is needed to confirm an association.
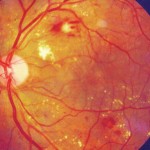
Diabetic retinopathy refers to changes in the retina (the back of the eye) caused by diabetes. Eye doctors check for retinopathy by dilating or enlarging the pupils with drops. Here’s 5 questions and answers that define and characterize the disease.

A direct, head-to-head comparison of two of the newer treatments available for type 2 diabetes yielded mixed results.
If you are diabetic, even small foot wounds have the potential for becoming serious ulcers that can lead to amputation if not properly treated.

Lilly says its once-weekly injectible drug, dulaglutide, has outperformed three other widely taken diabetes drugs in three just-concluded Phase III studies.
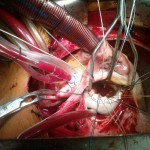
Adults with diabetes and multi-vessel coronary heart disease who underwent cardiac bypass surgery had better overall heart-related outcomes than those who underwent an artery-opening procedure to improve blood flow to the heart muscle.
J. Segura of Hospital Universitario 12 de Octubre, Madrid, España and colleagues published a study recently in Medicica and Clinica saying that patients with both hypertension and type 2 diabetes were more likely than those with only hypertension to develop cardiovascular disease.

Adults who gained weight during the first year following their initial diagnosis with type 2 diabetes had a significantly increased risk for cardiovascular-disease death and for all-cause death

Is exercise and diet enough? A diabetic’s personal experience.
Bariatric surgery, which significantly curtails the amount of food a person can eat, is the most effective treatment against obesity.
It’s a precursor to diabetes, but it also can be reversed. Insulin resistance is a fuzzy, often misunderstood concept. Here, we answer five common questions.
Bariatric surgery for diabetes treatment was selected as the most important medical innovation for 2013 in a poll of Cleveland Clinic physicians and researchers.

Exercise plays an important role in diabetes management, but people with either type 1 or type 2 diabetes should take certain precautions before increasing their level of physical activity, experts say.
Type 2 diabetes mellitus and insulin treatments may increase risk of lung cancer in diabetics, according to some studies.

Having diabetes mellitus type 2 increases the risk of developing breast cancer and death from all causes in older women and non-white women, according to a new study in Cancer Causes and Control.

The primary underlying cause of diabetes appears to be low-level, systemic inflammation, which can result from myriad lifestyle choices.

Patients who had suboptimal glycemic control and reduced their HbA1c value by slightly less than 1% were 50% less likely to die within 5 years than were patients whose HbA1c did not improve.
Blood glucose monitoring at least once a day is associated with reduced A1C levels and greater adherence to medication in type 2 diabetes patients who do not take insulin